- Advisory on choosing a cloud SaaS (ERP, EPM, SCM, CRM/CX, Data and BI/Analytics), PaaS (Integration ( API, Microservices, SOA Webservices), IaaS platforms
- Cloud Strategy and Vision:
- Technical strategy objective: Establish scalable technical strategies, beyond a minimum viable product, so customers can easily customize and adapt to meet their needs and address common constraints.
- Business strategy objective: Without defining business strategy in this guidance, we will help architects understand, document, and communicate the business strategy so the right decisions can be made.
- Culture strategy objective: While not providing deep guidance on facilitating culture or organizational change, we will provide methodologies, scenarios, and questions that will help identify and remove cultural roadblocks to the technical strategy.
- Cloud Business Cases – 3/5/7 year cost benefit modelling showing ROI, NPV, TCO, IRR and Payback with direct and indirect benefits outlined
- Cloud Architecture documentation – roadmaps, TOGAF blueprints and architecture styles, patterns and design best practices.
- Cloud Adoption Framework facilitation: To successfully adopting the cloud, a customer must prepare its people, technologies, and processes for this digital transformation inclusive of the following stages which our cloud architects will facilitate:
- Plan: Align business outcomes to actionable technology backlogs. This phase consists of three areas of early stage planning activities:
- Define the business justification and business outcomes.
- Prioritise workloads based on impacts to the business outcomes.
- Create a cloud adoption plan based on the current digital estate and prioritised workloads.
- Ready: Prepare the people, culture, and environment for change. This phase has three key components:
- Create a cloud strategy team and other organisational alignment.
- Create a skills readiness plan across roles and functions.
- Establish a foundation by preparing the cloud environment.
- Adopt: Implement the desired changes across IT and business processes to help customers realize their business, technology, and people strategies. This phase includes several areas that will vary depending on what the organisation is implementing:
- Migration of workloads and assets.
- Apps and data modernisation.
- Cloud governance.
- Management and operation of assets and workloads in the cloud.
- Plan: Align business outcomes to actionable technology backlogs. This phase consists of three areas of early stage planning activities:
- These phases are not linear and will likely become a cycle, with customers revisiting and expanding adoption plans as their people become more cloud proficient and their apps and workloads are properly managed and operated, aligned with corporate policies, and deliver on their business outcomes.
- Data Lifecycle – Integration/Ingestion, Processing, Storage, Analysing (Data Science) and Visualisation/Dashboarding/Reporting
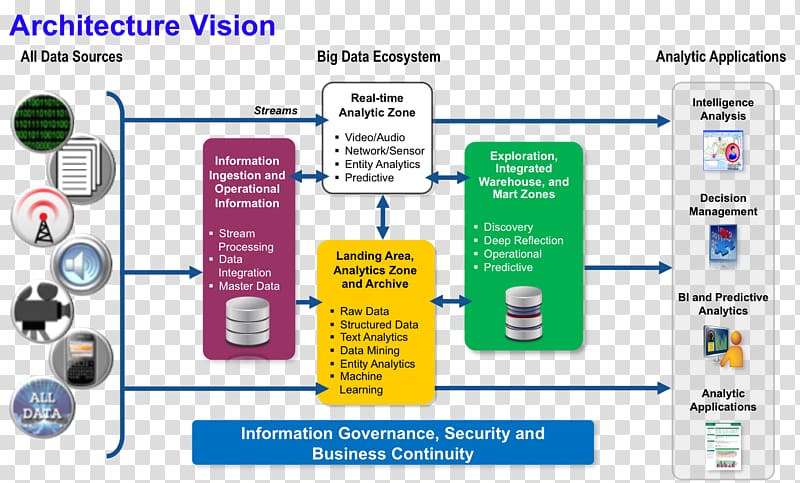
Design and Deployment if Modern Data Architectures in the Cloud
- Cloud Adoption Roadmap: Guide clients through the journey of migrating data and applications to the cloud, considering factors like cost, security, and performance.
- Data Architecture Design of scalable and secure data architectures on chosen cloud platforms AWS, Azure, or GCP, tailored to specific business needs.
- Data Migration Services: Assist with migrating data from on-premises databases, legacy systems, or other cloud platforms to the chosen cloud environment.
- Setup and Configuration of Big Data workloads: Batch processing of big data sources at rest; Real-time processing of big data in motion;Interactive exploration of big data; utilise cloud-based big data analytics and machine learning tools to extract insights from data and drive business decisions.
- Data Lake Management: Design and manage cloud data lakes for storing and processing large volumes of unstructured data.
- Data Mesh services to help businesses design and implement distributed data ownership models, self-service data access, and automated data pipelines.
- Design and Configuration of Cloud Data pipelines.
Agile Discovery, Prototype and Go Live Service Delivery Management
- Align to Scrum or Kanban methodologies using JIRA and/or Trello (if feasible in your organisation)
- Coach and mentor teams in Agile practices
- Establish success metrics, identify risks and dependencies
- Run all key agile ceremonies as scrum master – daily standups, retrospectives, sprint planning and reviews
- Document and version control in central repository all agile artefacts – user stories, product backlogs, burn-down charts, project gant and delivery velocity, reports/scorecards, sprint reviews, daily standup, blockers/challenges and risks, project budget costs vs actuals
- Develop the scope of what you’re going to build
- Identify legacy issues/blockers within your organisation that may impact technical aspects
- Speak to service delivery staff and policy owners to get an understanding of the existing business process
- Determine if any policy that relates to your service might prevent you from delivering a good service to your users
- Make sure stakeholders understand the project and have provided approval
- Do regular presentations or showcases to show stakeholders what you’ve learned
- Build & Test prototypes of your service with users
- Demonstrate the service you want to build is technically possible
- Presentation (showcase) to show the team and stakeholders (Product Owner/s) what you’ve learned and what you have developed so far.
- Demo and continuous iterations until demonstrate your prototypes meet the user need – Build a working service that can be used in full by users.